special tests for mcl tear|proximal medial collateral ligament tear : sourcing Phase 1: Weeks 0-2. PRECAUTIONS. Screen for fractures with Ottawa Knee Rules. Assess for injury to supporting structures. Anterior cruciate ligament. Posterior cruciate ligament. Medial . Futebol em directo. Liga Profesional Argentina em directo. Calendário Liga Profesional Argentina e jogos amanhã (Futebol - Argentina) QuotasResultados. Não há Liga Profesional Argentina em direto atualmente. Não há jogos amanhã de Liga Profesional Argentina de Futebol. Veja os jogos dos dias anteriores.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB17 de jan. de 2024 · 12:00-23:00. Seu pai bar & drinkeria, #192 entre Belo Horizonte pubs & bares: 1594 avaliações e 15 fotos detalhadas. Encontrar no mapa e ligar para reservar .
The valgus stress test, also known as the medial stress test, is used to assess the integrity of the medial collateral ligament (MCL) of the knee. MCL injuries are common in the athletic . A medial collateral ligament (MCL) knee injury is a traumatic knee injury that typically occurs as a result of a sudden valgus force to the lateral aspect of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected with increased valgus laxity . Your physical therapist also will perform special tests to help determine the likelihood that you have an MCL injury. Your therapist will gently press on the outside of your knee while it is slightly bent as well as when it is .Phase 1: Weeks 0-2. PRECAUTIONS. Screen for fractures with Ottawa Knee Rules. Assess for injury to supporting structures. Anterior cruciate ligament. Posterior cruciate ligament. Medial .
A medial knee ligament sprains (MCL) is a tear of the ligament on the inside of the knee. In order to diagnose an MCL sprain your physio or doctor performs a number of tests including the valgus stress test. Knee ligament .
What tests will be done to diagnose an MCL tear? Your healthcare provider may use one or more of the following tests to diagnose an MCL tear: Physical exam: Your provider .
The assessment includes palpation and a special test, the valgus stress test VST Palpation; The anterior aspect of the ligament can be palpated moving vertically, roughly midway along the medial joint line. Focal tenderness .
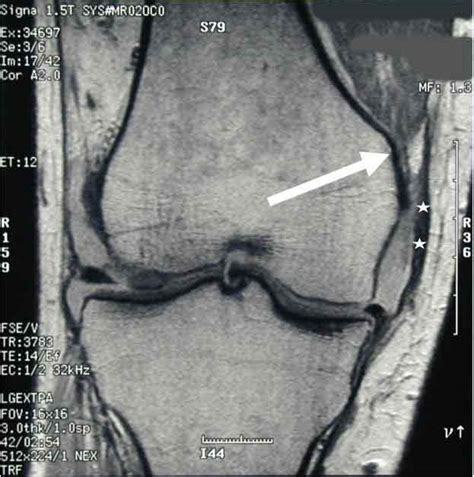
Injuries of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), also referred to as the tibial collateral ligament, occur frequently in athletes, particularly those involved in sports that . MCL Tear Grading. If you have an MCL tear, your health care professional will rate how serious your injury is by using one of these three grades: Grade 1 is a mild tear.
Pages in category "Knee - Special Tests" The following 26 pages are in this category, out of 26 total. A. Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury; Anterior Drawer Test of the Knee; Apley's Test; B. Beighton score; D. Dial Test; E. Effusion tests of the Knee; Ege's Test; Ely's Test; I. Insall-Salvati Ratio; L. Lachman Test;The knee joint allows the lower leg to flex (bend) or straighten (extend). To make certain that those are the only two motions that occur, four ligaments in the knee help control and protect it. The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is located on the medial aspect of the knee (medial = the closest to the center of the body) or inside of the knee.; The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is .
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is a flat band of connective tissue that runs from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle of the tibia. Its role is to provide valgus stability to the knee joint. MCL injuries often occur in sports, especially in skiing; in fact, 60% of skiing knee injuries involve the MCL. [1][2][3]
The medial collateral ligament, commonly referred to as the MCL, is a thick and strong ligament located along the inner side of the knee. The MCL stretches from the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone) and helps to stabilize the medial (inner) part of the knee.Diagnostic Imaging . A doctor may order one or more medical imaging tests to confirm the presence and determine the severity of an MCL injury. X-rays use low levels of radiation and give doctors a view of a person’s bones. Although MCL injuries do not show up on standard X-ray exams, they are a relatively inexpensive, fast way to rule out other possible injuries that might .Meniscus tears are the most common injury of the knee. Medial meniscus tears are generally seen more frequently than tears of the lateral meniscus, with a ratio of approximately 2:1. [2] Meniscal tears may occur in acute knee injuries in younger patients or as part of a degenerative process in older individuals.
Edson CJ. Conservative and postoperative rehabilitation of isolated and combined injuries of the medial collateral ligament. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2006;14(2):105-110.The test is performed in conjunction with the Apley's distraction test. Meniscal injuries are very common and are associated with significant pain and morbidity. . and the medial collateral ligament (MCL). When performing a physical examination, joint line tenderness, joint effusion, and impaired range of motion are the most common findings .Medial Collateral ligament injury [edit | edit source] . An adjunct to the clinical special tests in assessing anterior translation is the use of instrumented laxity testing. The most commonly cited arthrometer is the KT1000 (Medmetric, San Diego, California). The arthrometer provides an objective measurement of the anterior translation of .
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is located on the inner side of your knee and connects the thigh bone (femur) and the shinbone (tibia). . but your doctor may also complete the following tests to see how bad the sprain or tear is: X-rays, which can help rule out further damage such as a broken or fractured bone. Magnetic resonance imaging .Medial collateral ligament tears often occur as a result of a direct blow to the outside of the knee. This pushes the knee inward (toward the other knee). . Other tests that may help your doctor confirm your diagnosis include: X-rays. Although they will not show any injury to your collateral ligaments, X-rays can show whether the ligament .Mechanism of injury is extremely important. If you can work out the force of the injury this gives you clues on likely stretched/ damaged structures (Valgus force may indicate an MCL sprain, varus force may indicate an LCL sprain, foot planted . INTRODUCTION. Injuries of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), also referred to as the tibial collateral ligament, occur frequently in athletes, particularly those involved in sports that require sudden changes in direction and speed, and in .
A grade 2 (moderate) MCL tear usually heals in 4-6 weeks with treatment. A grade 3 (severe) MCL tear usually takes 6 weeks or longer to heal with treatment. If you have surgery, it can take more time. Pain from an isolated MCL injury can limit active motion, particularly terminal knee extension and flexion beyond 100 degrees; Isolated MCL injury generally does not constrain passive range of motion; Special .The medial collateral ligament, or MCL, can be sprained or torn from a blow to the outer side of the knee when twisting the knee or by a quick direction change while walking or running. . Your physical therapist also will perform special tests to help determine if you have an MCL injury. They will gently press on the outside of your knee . The lateral and medial menisci are crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structures that collectively cover approximately 70% of the articular surface of the tibial plateau and primarily function in load transmission and shock absorption through the tibiofemoral joint. They are wedge-shaped with thicker portions at the periphery of the joint, thereby deepening the articular .
Injuries to the PCL often occur with other knee structures (ligaments, meniscus) while infrequently occurring in isolation. PCL injury alone accounts for approximately 2 per 100,000 people annually. Injury to the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) can range from a stretch to a total tear or rupture of the ligament. ONLINE COURSES: https://study.physiotutors.comGET OUR ASSESSMENT BOOK ︎ ︎ http://bit.ly/GETPT ︎ ︎OUR APPS: 📱 iPhone/iPad: https://apple.co/35vt8Vx🤖 Andro.
One of the most common special tests performed to determine if there is an MCL injury is a valgus stress test. During this test, the leg is positioned in such a way that places intentional stress on the medial collateral ligament. A positive test is present if there is excessive laxity or medial joint gapping with or without pain. Imaging Tests
There are an estimated 80,000 to 100,000 anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) repairs in the United States each year. Most ACL tears occur from noncontact injuries. Women experience ACL tears up to .Of the collateral ligament injuries, MCL injuries are more commonly seen over LCL injuries. Limited studies have shown that isolated LCL injuries occur more often in women and in high contact sports. . Varus Stress Test-The most useful special test when assessing a LCL injury. With the femur stabilized, a varus force is applied with special . Clinical trials. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.. Preparing for your appointment. The pain and disability associated with an ACL injury prompt many people to seek immediate medical attention. Others may make an appointment with their family doctors. The medial collateral ligament, or MCL, of the knee can tear due to injury and cause pain. . A doctor might carry out further imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis. . Physical therapist's .
Apley's grind test (patellar cartilage tear): By placing palm on patella and applying firm pressure while manipulating the patella in the sagittal plane. Crepitus is significant only when accompanied by tenderness, in which case it is consistent with patellar cartilage pathology.Special Tests: These should only be performed if relevant and help to confirm the diagnosis. Nerve root compression tests; . tape, and therapy. A recent report detailing the efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in effectively treating medial collateral ligament injuries in throwers has shown promise. However, there remain specific groups that .
acetabular labral tear orthopedic test
WEBWelcome to. Remember my username or card number. Need help signing in?
special tests for mcl tear|proximal medial collateral ligament tear